NASA: West Antarctic Ice Sheet Melt Has Begun And Is Unstoppable
Posted on: Wednesday, May 21, 2014
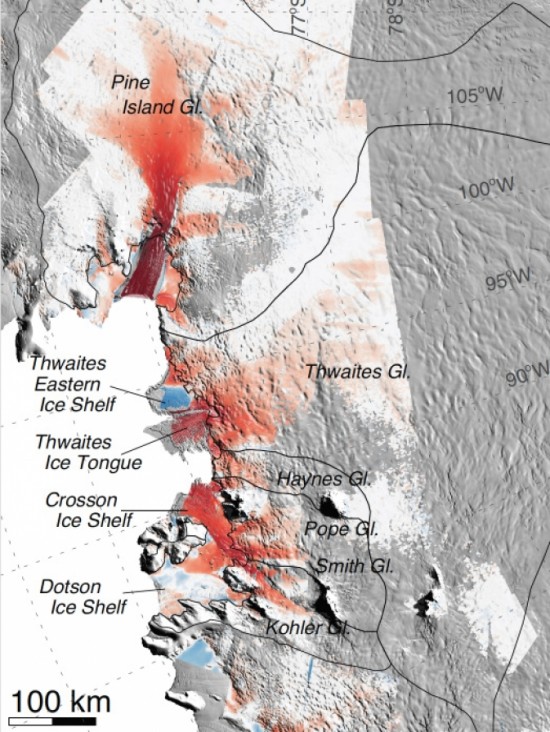
A new study by researchers at NASA and the University of California, Irvine, finds a rapidly melting section of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet appears to be in an irreversible state of decline, with nothing to stop the glaciers in this area from melting into the sea.
The study presents multiple lines of evidence, incorporating 40 years of observations that indicate the glaciers in the Amundsen Sea sector of West Antarctica "have passed the point of no return," according to glaciologist and lead author Eric Rignot, of UC Irvine and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The new study has been accepted for publication in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
These glaciers already contribute significantly to sea level rise, releasing almost as much ice into the ocean annually as the entire Greenland Ice Sheet. They contain enough ice to raise global sea level by 4 feet (1.2 meters) and are melting faster than most scientists had expected. Rignot said these findings will require an upward revision to current predictions of sea level rise.
VIsit NASA.gov and see this great background article on The "Unstable" West Antarctic Ice Sheet: A Primer